How to install Bareos on Ubuntu 20.04
Bareos is a clone of Bacula.org that is a true open source backup platform. It’s a free, enterprise-ready open source backup solution for companies and people searching for a more straightforward approach to manage their backups.
Ubuntu is a free and open source Linux operating system that may be installed on computers, laptops, servers, and other devices. When learning Ubuntu, you’ll discover that it’s similar to Windows and other operating systems in a lot of respects, especially when it comes to getting work done.
Update Ubuntu 20.04
You must first update Ubuntu before installing software packages. Execute the following commands to do so:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt dist-upgrade
$ sudo apt autoremove
This should bring Ubuntu up to date and remove any outdated packages from your system. It’s also a good idea to reset the computer after you’ve finished updating.
Repository for Bareos
After you’ve upgraded Ubuntu, you’ll need to add the Bareos repository and key file to your computer. Newer packages will be made available to your machine as soon as its repository is added.
Run the instructions below to add the repository with the most recent packages and key:
For Ubuntu 20.04
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://download.bareos.org/bareos/release/latest//xUbuntu_20.04 /" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/bareos.list'For Ubuntu 18.04
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://download.bareos.org/bareos/release/latest//xUbuntu_18.04 /" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/bareos.list'After you’ve added the repository, run the instructions following to import the repository’s GPG key:
$ wget -q http://download.bareos.org/bareos/release/latest/xUbuntu_16.04/Release.key -O- | sudo apt-key add -Run the scripts below to update the Ubuntu package list index and install Bareos with MariaDB database server after adding the repository and key above.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server bareos bareos-database-mysql
When prompted to configure Postfix, select “Internet site” from the drop-down menu.
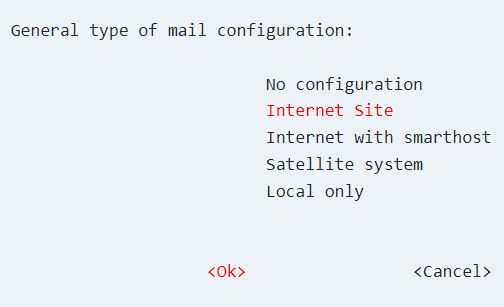
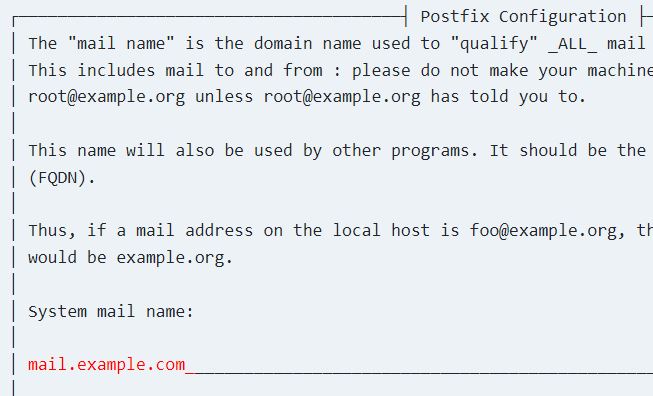
For system mail, choose a server name.
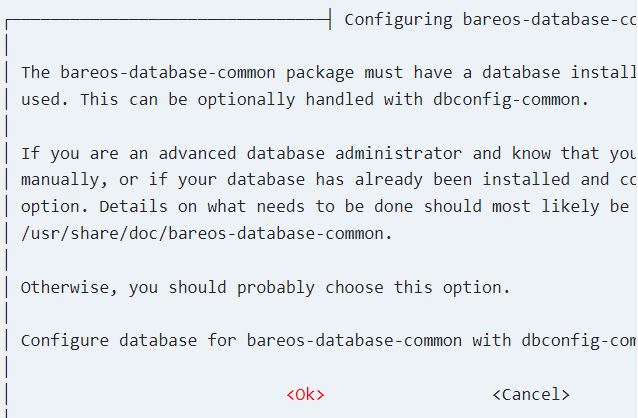
Select a database component for Bareos to install.
Then, for the database root user, generate and confirm a new password.

After you’ve set everything up, run the instructions below to start the Bareos daemon services:
$ sudo systemctl bareos-dir start
$ sudo systemctl bareos-sd start
$ sudo systemctl bareos-fd start
Bareos Web UI
The Bareos WebUI is a component of the Bareos project that is available on a variety of platforms. It’s a PHP-based front end for managing and monitoring Bareos jobs and resources. Run the scripts following to install the Web UI:
$ sudo apt install bareos-webuiApache web server, PHP, and a variety of extensions are among the dependencies installed. To activate the updated configuration, restart the Apache web server.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2To start other Bareos services, use the commands listed below.
$ sudo systemctl start bareos-dir bareos-sd bareos-fdCreate console user
You’ll need to create a user to access the Bareos web portal if you want to connect to it. To create a new user, open the Bareos console with the commands below.
$ sudo bconsoleTo create a new user, sign in and run the commands below.
*relaod
*configure add console name=admin password=admin_user_password_here profile=webui-admin tlsenable=false
After that, you should get something similar to this:
Created resource config file “/etc/bareos/bareos-dir.d/console/admin.conf”:
Console {
Name = admin
Password = admin_user_password
Profile = webui-admin
TlsEnable = false
}
Apache2 should be used to exit and restart Bareos services.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2 bareos-dir bareos-sd bareos-fdWhen you’re finished, go to your web browser and type /bareos-webui followed by the server hostname or IP address.
http://localhost/bareos-webui












